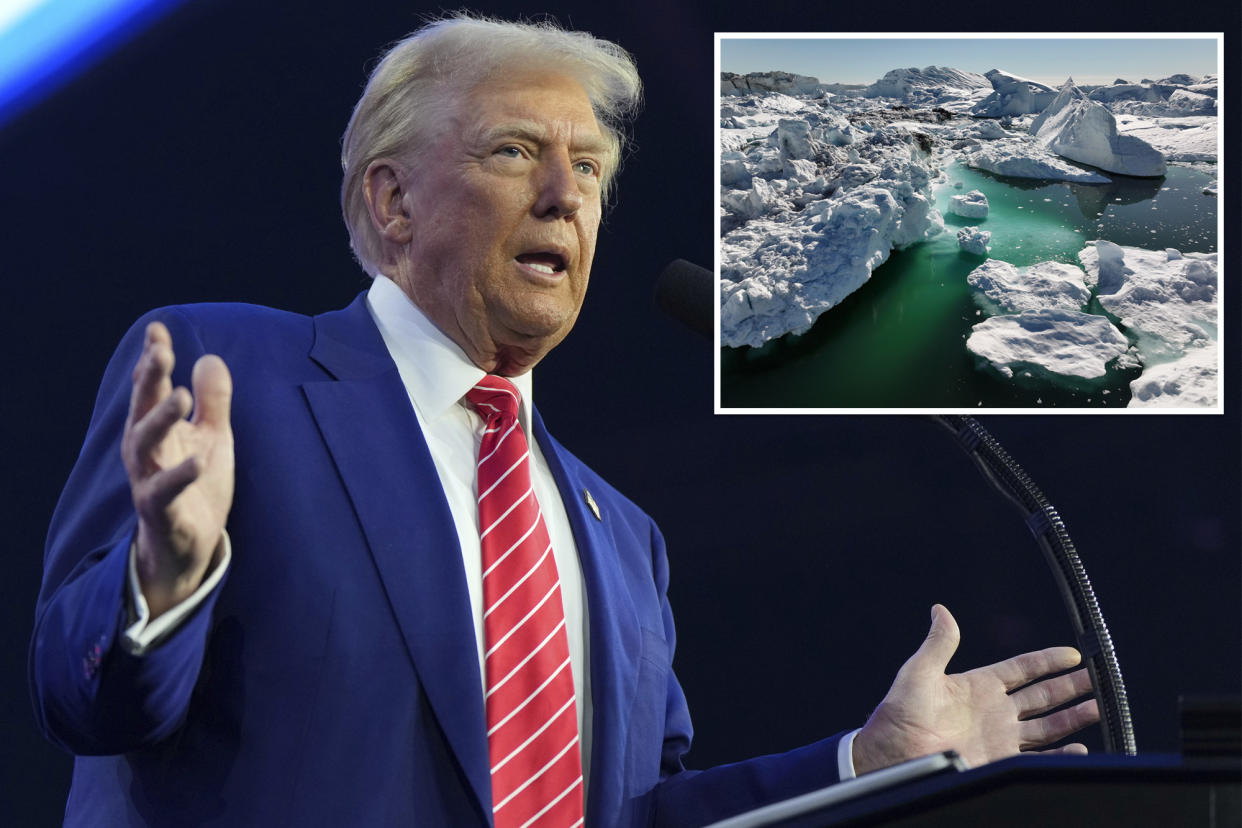
WASHINGTON, D.C. — President Donald Trump’s renewed interest in purchasing Greenland underscores America’s strategic focus on the Arctic. The autonomous Danish territory has become a critical geopolitical chess piece, drawing intense interest from the U.S., China, and Russia. Trump has refused to rule out using economic or military leverage to secure Greenland, further spotlighting its growing importance.
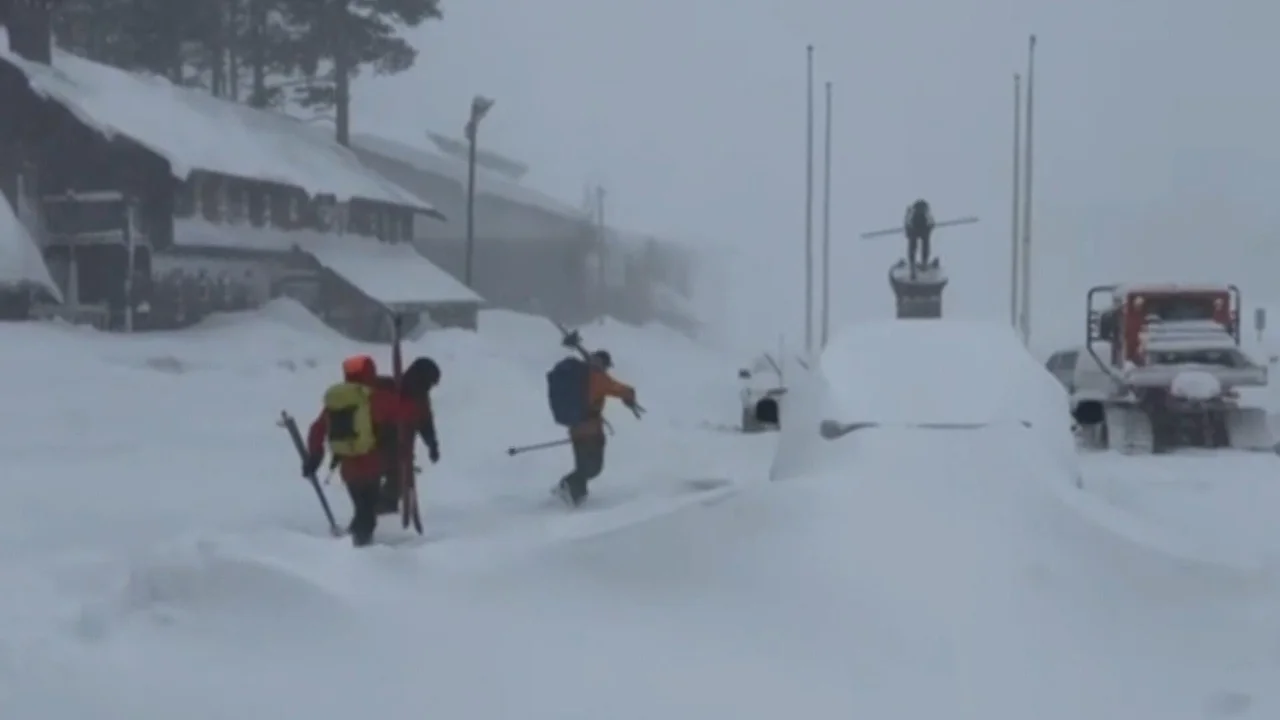
Greenland’s appeal is more than territorial—it’s about control of the Arctic, a region rich in resources and crucial for military and economic dominance.

Arctic Hotspot: A Geopolitical Tug-of-War
The United States faces competition in its Arctic ambitions. In 2018, a Chinese state-owned firm attempted to invest $550 million to expand two Greenlandic airports. The bid, which would have increased Beijing’s Arctic influence, was ultimately withdrawn under pressure from Denmark and the U.S.
Russia, meanwhile, has reopened several Cold War-era military bases in the Arctic, including Nagurskoye, just 600 miles north of Greenland. This resurgence of Russian military activity reflects the region’s strategic significance for defense and energy resources.
“Greenland is ground zero for the Arctic’s growing geopolitical importance,” explained Klaus Dodds, a geopolitics professor at Royal Holloway, University of London.

The U.S. Strategic Edge: Geography Meets Defense
Greenland’s location provides the U.S. with a strategic advantage, particularly for its ballistic missile warning systems. As China triples the size of its intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) arsenal, Greenland’s geography becomes even more critical.
“With the Arctic’s shifting dynamics and China’s growing missile capabilities, Greenland is vital to U.S. national defense,” said Brent Sadler, a senior research fellow at the Heritage Foundation.
The Arctic also offers economic opportunities. Shipping routes through the region have increased by 37% over the past decade, according to the Arctic Council. Greenland’s proximity to these routes positions it as a gateway for lucrative maritime trade.

China’s Polar Silk Road and Russia’s Arctic Revival
In 2018, China unveiled plans for a “Polar Silk Road,” connecting Asia to Europe via Arctic waters. As melting ice opens up new shipping lanes, Beijing sees the Arctic as a key piece of its Belt and Road Initiative.
Russia, on the other hand, is focusing on militarizing the Arctic. With advanced bases and icebreaker fleets, Moscow is positioning itself as a dominant Arctic power.

Economic and Environmental Stakes
The melting Arctic ice cap is not just altering global shipping; it’s unlocking untapped oil, gas, and mineral reserves. The U.S., China, and Russia are all eyeing these resources, intensifying the race for Arctic control.
“As the Arctic ice continues to retreat, the region’s economic and strategic potential grows exponentially,” Sadler added.
What’s Next for Greenland?
Trump’s aggressive stance on Greenland reflects a broader strategy to counter China and Russia in the Arctic. Whether through diplomatic negotiations or economic measures, the U.S. appears determined to maintain its foothold in the region.
Greenland, once seen as a remote icy expanse, has now become a focal point in the 21st-century battle for global power and resources.